Go语言HTTP请求流式写入body的示例代码
背景
最近在开发一个功能时,需要通过 http 协议上报大量的日志内容,但是在 Go 标准库里的 http client 的 API 是这样的:
http.NewRequest(method, url string, body io.Reader)
body 是通过 io.Reader 接口来传递,并没有暴露一个 io.Writer 接口来提供写入的办法,先来看看正常情况下怎么写入一个 body ,示例:
需要先把要写
buf := bytes.NewBuffer([]byte("hello"))
http.Post("localhost:8099/report","text/pain",buf)
入的数据放在 Buffer 中,放内存缓存着,但是我需要写入 大量 的数据,如果都放内存里肯定要 OOM 了,http client 并没有提供 流式写入 的方法,我这么大的数据量直接用 Buffer 肯定是不行的,最后在 google 了一番之后找到了解决办法。
使用 io.pipe
调用 io.pipe() 方法会返回 Reader 和 Writer 接口实现对象,通过 Writer 写数据, Reader 就可以读到,利用这个特性就可以实现流式的写入,开一个协程来写,然后把 Reader 传递到方法中,就可以实现 http client body 的流式写入了。
代码示例:
pr, rw := io.Pipe()
// 开协程写入大量数据
go func(){
for i := 0; i < 100000; i++ {
rw.Write([]byte(fmt.Sprintf("line:%d\r\n", i)))
}
rw.Close()
}()
// 传递Reader
http.Post("localhost:8099/report","text/pain",buf)
源码阅读 目的
了解 go 中 http client 对于 body 的传输是如何处理的。
开始
在构建 Request 的时候,会断言 body 参数的类型,当类型为 *bytes.Buffer 、 *bytes.Reader 、 *strings.Reader 的时候,可以直接通过 Len() 方法取出长度,用于 Content-Length 请求头,相关代码net/http/request.go#L872-L914 :
if body != nil {
switch v := body.(type) {
case *bytes.Buffer:
req.ContentLength = int64(v.Len())
buf := v.Bytes()
req.GetBody = func() (io.ReadCloser, error) {
r := bytes.NewReader(buf)
return ioutil.NopCloser(r), nil
}
case *bytes.Reader:
req.ContentLength = int64(v.Len())
snapshot := *v
req.GetBody = func() (io.ReadCloser, error) {
r := snapshot
return ioutil.NopCloser(&r), nil
}
case *strings.Reader:
req.ContentLength = int64(v.Len())
snapshot := *v
req.GetBody = func() (io.ReadCloser, error) {
r := snapshot
return ioutil.NopCloser(&r), nil
}
default:
}
if req.GetBody != nil && req.ContentLength == 0 {
req.Body = NoBody
req.GetBody = func() (io.ReadCloser, error) { return NoBody, nil }
}
}
在链接建立的时候,会通过 body 和上一步中得到的 ContentLength 来进行判断,如果 body!=nil 并且 ContentLength==0 时,可能就会启用 Chunked 编码进行传输,相关代码 net/http/transfer.go#L82-L96 :
case *Request:
if rr.ContentLength != 0 && rr.Body == nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("http: Request.ContentLength=%d with nil Body", rr.ContentLength)
}
t.Method = valueOrDefault(rr.Method, "GET")
t.Close = rr.Close
t.TransferEncoding = rr.TransferEncoding
t.Header = rr.Header
t.Trailer = rr.Trailer
t.Body = rr.Body
t.BodyCloser = rr.Body
// 当body为非nil,并且ContentLength==0时,这里返回-1
t.ContentLength = rr.outgoingLength()
// TransferEncoding没有手动设置,并且请求方法为PUT、POST、PATCH时,会启用chunked编码传输
if t.ContentLength < 0 && len(t.TransferEncoding) == 0 && t.shouldSendChunkedRequestBody() {
t.TransferEncoding = []string{"chunked"}
}
验证(一)
按照对源码的理解,可以得知在使用 io.pipe() 方法进行流式传输时,会使用 chunked 编码进行传输,通过以下代码进行验证:
服务端
func main(){
http.HandleFunc("/report", func(writer http.ResponseWriter, request *http.Request) {
})
http.ListenAndServe(":8099", nil)
}
客户端
func main(){
pr, rw := io.Pipe()
go func(){
for i := 0; i < 100; i++ {
rw.Write([]byte(fmt.Sprintf("line:%d\r\n", i)))
}
rw.Close()
}()
http.Post("localhost:8099/report","text/pain",buf)
}
先运行服务端,然后运行客户端,并且使用 WireShake 进行抓包分析,结果如下:

可以看到和预想的结果一样。
验证(二)
在数据量大的时候 chunked 编码会增加额外的开销,包括编解码和额外的报文开销,能不能不用 chunked 编码来进行 流式传输 呢?通过源码可以得知,当 ContentLength 不为 0 时,如果能预先计算出待传输的 body size ,是不是就能避免 chunked 编码呢?思路就到这,接着就是写代码验证:
服务端
func main(){
http.HandleFunc("/report", func(writer http.ResponseWriter, request *http.Request) {
})
http.ListenAndServe(":8099", nil)
}
客户端
count := 100
line := []byte("line\r\n")
pr, rw := io.Pipe()
go func() {
for i := 0; i < count; i++ {
rw.Write(line)
}
rw.Close()
}()
// 构造request对象
request, err := http.NewRequest("POST", "http://localhost:8099/report", pr)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
// 提前计算出ContentLength
request.ContentLength = int64(len(line) * count)
// 发起请求
http.DefaultClient.Do(request)
抓包结果:
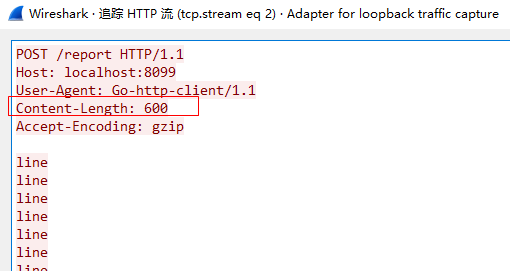
可以看到确实直接使用的 Content-Length 进行传输,没有进行 chunked 编码了。
总结
本文的目的主要是记录 go 语言中 http client 如何进行流式的写入,并通过阅读源码了解 http client 内部对 body 的写入是如何进行处理的,通过两个验证可以得知,如果能提前计算出 ContentLength 并且对性能要求比较苛刻的情况下,可以通过手动设置 ContentLength 来优化性能。
关于Go语言HTTP请求流式写入body的文章就介绍至此,更多相关Go语言HTTP请求内容请搜索编程宝库以前的文章,希望大家多多支持编程宝库!
go第三方库 github.com/spf13/viper 实现了对配置文件的读取并注入到结构中,好用方便。其中以viperInstance := viper.New() // vipe ...